Industrial components often fail when metals or polymers face extreme mechanical stress or corrosive heat. These limitations lead to frequent downtime and replacement costs that devastate your quarterly performance. High-performance zirconia ceramics provide a transformative alternative, offering the highest fracture toughness and chemical inertness available to ensure structural integrity where other materials simply fail.
Defining Zirconia Ceramics

Zirconia ceramics are crystalline oxides of zirconium chemically stabilized to provide extreme fracture toughness and corrosion resistance. These materials use a unique phase transformation to stop cracks from spreading through the matrix.
What makes this material unique?
Here is the deal: The primary differentiator is “transformation toughening,” which actively compresses crack tips to prevent failure.
- High-purity zirconium dioxide base.
- Integrated stabilizing oxides.
- Active crack-stopping mechanism.
Key Takeaway: Understanding phase transformation is fundamental to leveraging zirconia’s durability in high-stress environments.
| Property | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | ZrO2 | |
| Mechanism | Phase Transformation |
The crystalline structure provides metal-like reliability in a ceramic form.
Benefits of Zirconia Ceramics
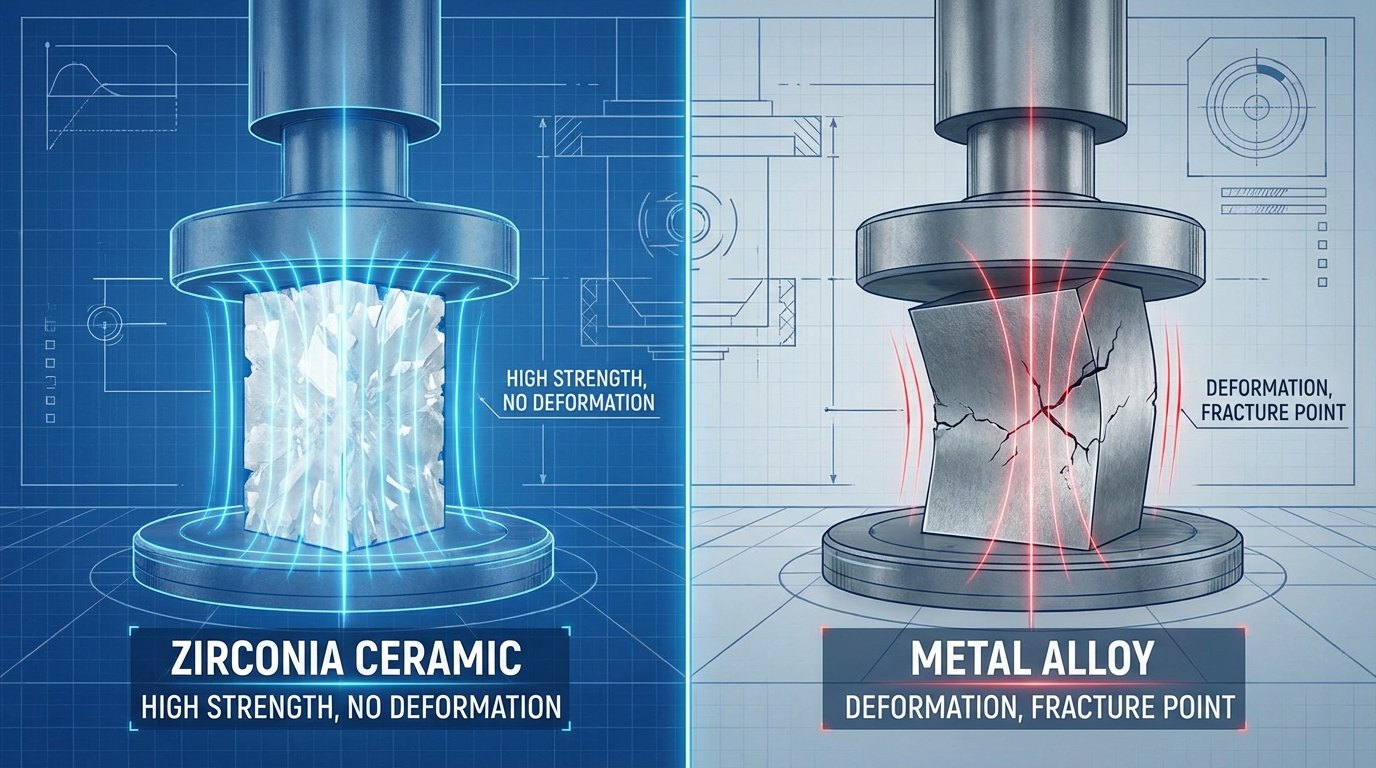
The primary benefits include metal-like mechanical strength, exceptional wear resistance, and the highest fracture toughness of any technical ceramic. You can replace brittle parts with components that handle intense impact without shattering.
Why is it stronger than metal?
Think about it: While metals deform under heat or pressure, these ceramics maintain geometry and surface finish under intense friction.
- Flexural strength exceeds alumina.
- Superior impact resistance.
- Non-magnetic properties.
Key Takeaway: Substituting metals with zirconia reduces maintenance frequency in abrasive industrial workflows.
| Advantage | Industrial Impact | |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Lower costs | |
| High Strength | Reliable support |
Strength remains consistent even when parts are subjected to corrosive chemicals.
Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics

Magnesia stabilized zirconia ceramics are engineered specifically to resist phase transformations at high temperatures while providing extreme toughness. This grade is your best defense against structural degradation in moist environments.
How does magnesia help?
Check this out: Adding magnesium oxide creates a microstructure that protects against grain boundary sliding during thermal cycles.
- Steam environment resistance.
- High impact threshold.
- Low thermal conductivity.
Key Takeaway: This grade is the preferred choice for high-moisture applications where other zirconias might degrade.
| Feature | MSZ Detail | |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture | High resistance | |
| Typical Use | Valve seats |
MSZ ensures stability in steam-heavy industrial processing.
Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics
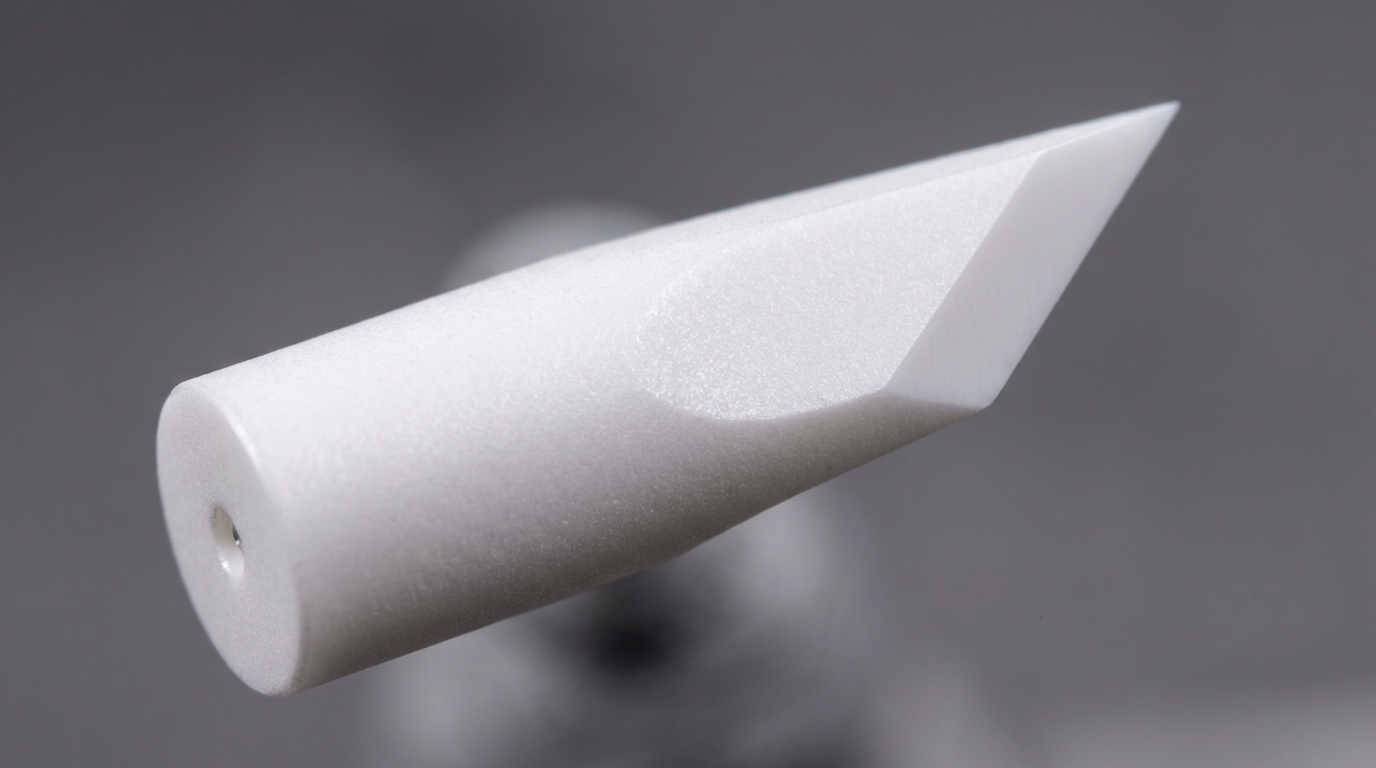

Yttria stabilized zirconia ceramics represent the highest strength grade, offering a fine-grained microstructure for maximum crack resistance. It is the industry standard for precision components requiring the absolute highest flexural strength.
When should you use yttria?
You might be wondering: If your application involves high-velocity fluids or sharp edges, this yttria-doped grade provides the necessary erosion resistance.
- Highest flexural strength.
- Fine surface finish.
- Superior erosion resistance.
Key Takeaway: While incredibly strong, keep yttria grades below 500°C to avoid property degradation.
| Property | YTZP Spec | |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Size | Fine | |
| Strength | Maximum |
YTZP provides the ultimate edge retention for industrial cutting tools.
Toughened Alumina Zirconia Ceramics

Toughened alumina zirconia ceramics (ZTA) blend the extreme hardness of alumina with the toughness of zirconia at an economical price. It offers a 20-30% strength increase over standard alumina without the full cost of pure zirconia.
Is ZTA cost-effective?
The bottom line is: You can bridge the performance gap between basic ceramics and high-end materials without exceeding your project budget.
- Lower cost than pure zirconia.
- Higher hardness than MSZ.
- Excellent for pump pistons.
Key Takeaway: ZTA is the smart choice for large structural parts requiring moderate toughening and high hardness.
| Comparison | ZTA vs Alumina | |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | 30% Higher | |
| Price | Mid-range |
ZTA balances affordability with high-performance mechanical specs.
Industrial Zirconia Ceramics Uses
Industrial uses for zirconia ceramics span aerospace, energy, and semiconductor sectors where parts must survive extreme environments. You will find them in everything from jet engine bearings to down-hole oil tools.
Which industries benefit?
It gets better: The non-magnetic and insulating nature of these ceramics makes them perfect for sensitive electronic handling and high-heat manufacturing.
- Aerospace bearings.
- Deep-well drilling tools.
- Semiconductor guides.
Key Takeaway: Versatility allows these ceramics to function as both thermal barriers and structural supports.
| Sector | Component | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | Fuel cell parts | |
| Aerospace | Thermal coatings |
Widespread industrial adoption stems from the material’s unique survival stats.
Thermal Stats of Zirconia Ceramics
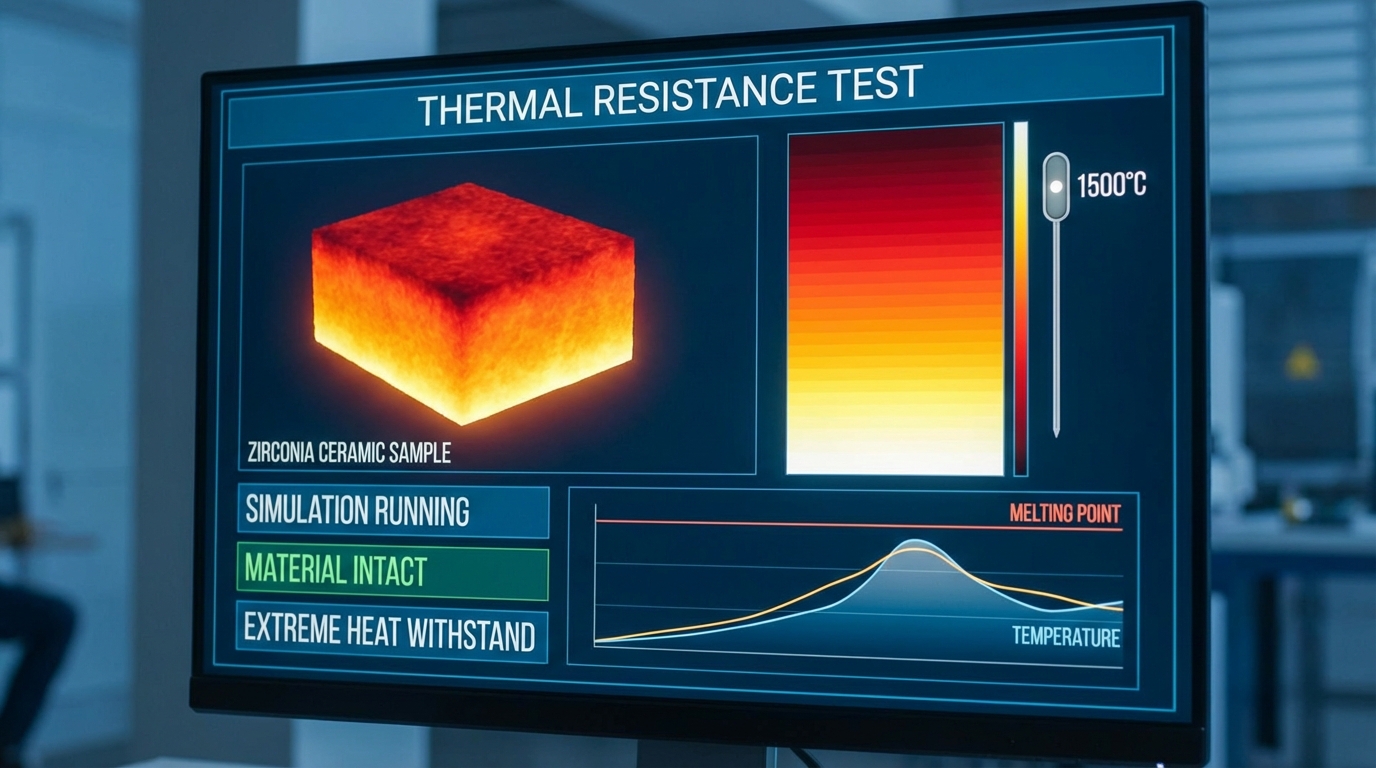
Thermal stats of zirconia ceramics highlight a low thermal conductivity and an expansion coefficient that closely matches cast iron. This thermal expansion compatibility makes ceramic-to-metal assemblies highly reliable across temperature swings.
Does heat impact integrity?
Truth be told: While zirconia acts as a natural heat barrier, you must select the right stabilizer to prevent steam-induced degradation.
- Conductivity: ~2 W/mK.
- Expansion: ~10 x 10⁻⁶/°C.
- Stable up to 1500°C (ZTA).
Key Takeaway: Matching the expansion of zirconia to metal housings prevents fitting failures during thermal cycling.
| Metric | Performance | |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Low/Insulating | |
| Match | Cast Iron |
Predictable thermal expansion simplifies the engineering of complex assemblies.
Medical Grade Zirconia Ceramics
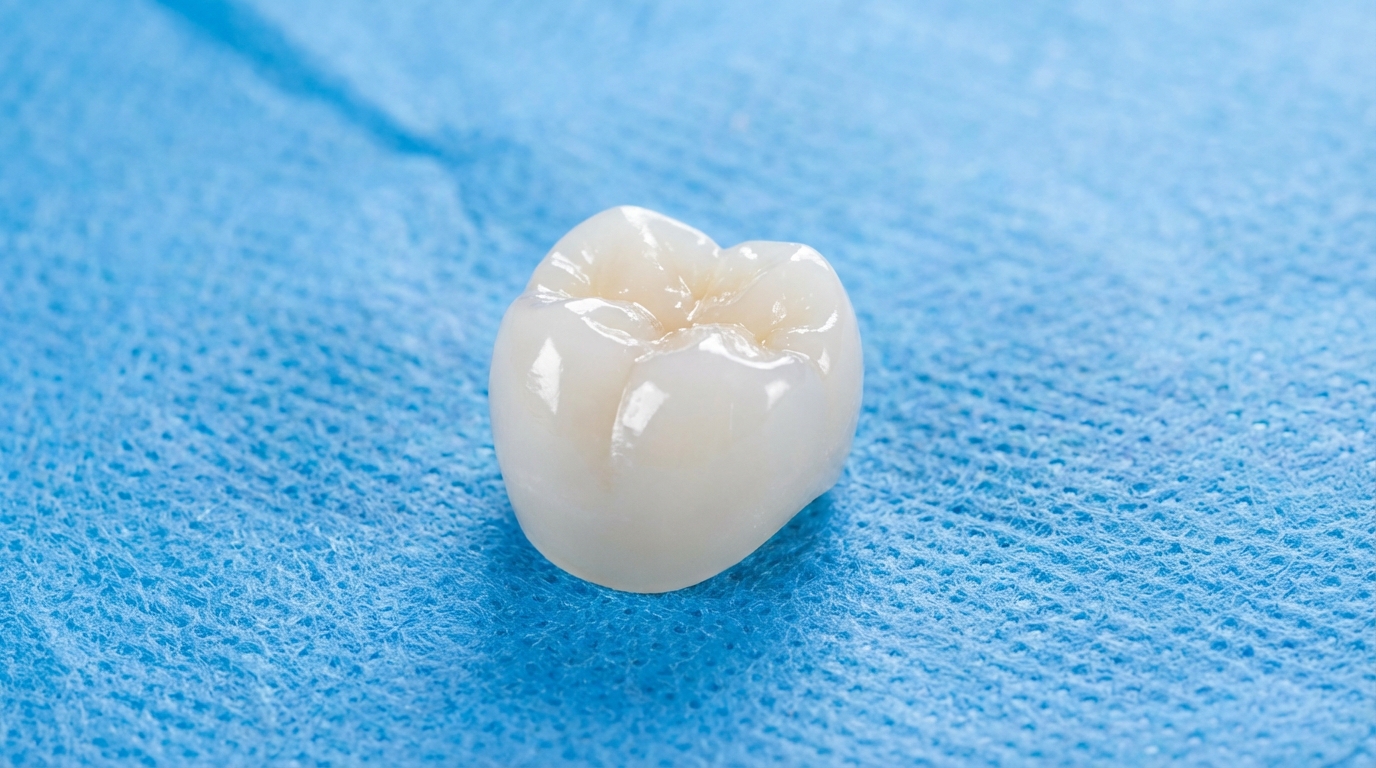
Medical grade zirconia ceramics are chosen for their extreme biocompatibility, high strength, and aesthetic qualities in implants. They do not trigger immune responses and remain chemically stable within the corrosive environment of the human body.
Why is biocompatibility preferred?
So, what’s next? Surgical tools and implants benefit from a non-metallic surface that resists bacterial growth and avoids metal sensitivity issues.
- Non-toxic and non-reactive.
- High wear resistance for joints.
- Natural aesthetic for dental.
Key Takeaway: Mechanical reliability combined with biological safety makes zirconia a staple for modern medical devices.
| Feature | Medical Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | Zero | |
| Durability | Long-term |
Zirconia implants provide a lifetime of service without structural fatigue.
Durable Wear in Zirconia Ceramics

The durable wear in zirconia ceramics far exceeds that of industrial plastics and most metal alloys. You gain a low-friction surface that resists slurry erosion, scouring, and abrasive particle loss.
How does it resist wear?
Looking closer: The high surface hardness ensures that particles cannot easily chip the surface, maintaining dimensional accuracy over time.
- Low-friction finish.
- Slurry erosion resistance.
- Minimal material loss.
Key Takeaway: Preserving dimensional accuracy ensures your precision systems remain calibrated for much longer periods.
| Wear Type | Resistance | |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive | Excellent | |
| Friction | Very Low |
Superior surface integrity extends the life of high-speed bearing systems.
Buying Guide for Zirconia Ceramics

Buying zirconia ceramics requires evaluating your operating temperature, moisture exposure, and required fracture toughness. You must choose a stabilizer—yttria, magnesia, or ceria—based on your specific environmental constraints.
How do you choose?
But wait—there is more: Always verify compliance data such as REACH and RoHS to ensure your components meet international safety standards.
- YTZP for max strength.
- MSZ for steam stability.
- ZTA for cost-efficiency.
Key Takeaway: Consult a specialist early to prevent selecting a grade that might degrade under your specific humidity.
| Factor | Grade | |
|---|---|---|
| High Heat | MSZ | |
| Peak Toughness | YTZP |
Proper grade selection eliminates the risk of premature component failure.
Conclusion: Engineering Reliability
Zirconia ceramics solve the most difficult material challenges by combining the strength of metals with the inertness of ceramics. By selecting the correct stabilized grade, you eliminate common failure points related to wear and thermal stress. Implement these advanced ceramic solutions into your next design to achieve higher operational reliability and a lower total cost of ownership. Reach out today to integrate the world’s toughest ceramic into your workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use zirconia in high-pressure steam?Yes. However, you must use Magnesia Stabilized Zirconia (MSZ), as yttria grades can degrade rapidly in water vapor between 200°C and 300°C.
What is the best grade for cutting blades?Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YTZP) is the best choice. It offers the highest flexural strength and maintains an incredibly sharp, durable edge.
Do these ceramic bearings need lubrication?No, not always. While lubrication helps heat dissipation, zirconia’s low friction and high hardness allow for dry operation in many specialized environments.
How does expansion match cast iron?Yes, it matches closely. The crystalline structure naturally expands at a rate similar to cast iron, which prevents ceramic-to-metal assemblies from loosening.
Are these materials environmentally safe?Yes. Quality zirconia ceramics are REACH and RoHS compliant, containing no toxic substances or heavy metals.